Medical schools are embracing 3D printing because it dramatically improves your learning experience through hands-on anatomical models that boost understanding by significant margins. You’ll practice surgical procedures on lifelike replicas without patient risk, reducing future operating times by an average of 62 minutes. The technology creates customized models for specialized fields like cardiology and neurology while saving institutions $3,720 per case compared to traditional methods. Continue exploring to discover how this innovation transforms medical education.
Enhanced Anatomical Learning Through Physical Models
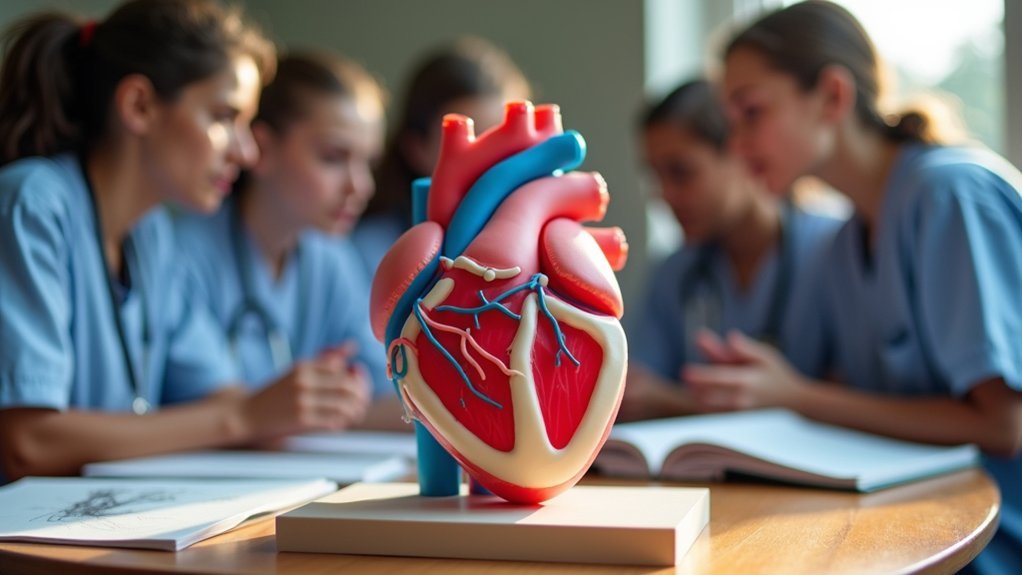

While traditional anatomical education has long relied on textbooks and cadaveric specimens, 3D printing technology is revolutionizing how you’ll learn complex medical structures in today’s classrooms.
These detailed anatomical models enhance your understanding of intricate body systems, delivering improved educational outcomes and higher test scores compared to conventional methods.
When you’re studying neuroanatomy, cardiac structures, or abdominal organs, 3D-printed models provide substantial learning improvements with standardized mean differences reaching 2.01 in abdominal anatomy alone.
You’ll experience increased satisfaction rates, as five out of six studies demonstrate higher student approval in the 3D group.
Medical schools are creating customized models that closely mimic patient-specific anatomy, making your education more relevant and applicable to real-world scenarios.
Improved Surgical Training and Skill Development
As you progress from studying anatomical models to developing hands-on surgical skills, 3D printing transforms your training experience by providing lifelike replicas that let you practice complex procedures before entering the operating room.
3D printing bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical surgical expertise through realistic, risk-free procedural rehearsal.
You’ll find these anatomical models offer unprecedented accuracy, allowing you to rehearse techniques repeatedly without patient risk. When you use 3D-printed surgical guides during training, you’re developing precision that translates directly to better patient outcomes and fewer complications in real procedures.
Studies demonstrate that surgical training with these models reduces your actual operating time by an average of 62 minutes, greatly improving efficiency.
You’ll also experience higher confidence levels compared to traditional training methods, while gaining deeper understanding of complex anatomical structures that enhance your overall surgical competency.
Customized Educational Tools for Different Medical Specialties
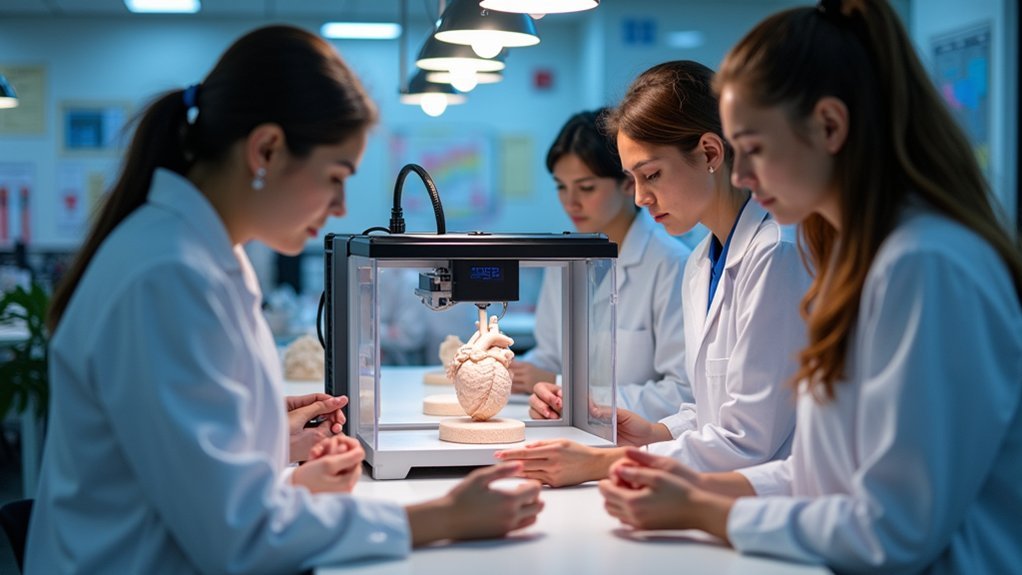

Beyond general surgical training, 3D printing technology adapts to meet the unique educational requirements of each medical specialty.
You’ll find that customized anatomical models allow students to focus on structures most relevant to their chosen field. Whether you’re studying cardiology, neurology, or orthopedics, these tailored educational tools provide detailed visualization of specific organs and systems critical to your specialty.
You can examine intricate cardiac chambers for cardiology training or explore complex neural pathways for neurosurgery preparation.
This personalized approach in medical education guarantees you’re studying exactly what you’ll encounter in practice. The customization extends beyond basic anatomy, incorporating pathological conditions and variations you’ll need to recognize and treat in your specialized field of medicine.
Cost-Effective Alternatives to Traditional Teaching Methods
Since traditional medical education methods often strain institutional budgets, you’ll discover that 3D printing transforms how schools approach cost management in medical training.
When you implement cost-effective 3D printing solutions, you’ll save $3,720 per case compared to traditional surgical preparation methods. You can create customized anatomical models tailored specifically to your curriculum needs, dramatically reducing expensive cadaver specimen requirements.
Through rapid prototyping capabilities, you’ll produce educational materials on-demand, eliminating costly inventory storage and reducing wait times.
You can manufacture complex, patient-specific models that lower your institution’s financial burden while enhancing student learning experiences. The technology enables you to produce surgical tools and educational resources at a fraction of traditional manufacturing costs, maximizing your educational budget’s impact while maintaining high-quality teaching standards.
Student Engagement and Hands-On Learning Opportunities

When medical students engage directly with 3D printing technology, they’re fundamentally transforming from passive learners into active creators of their educational materials.
You’ll find that this hands-on approach dramatically increases student engagement as learners design and print their own anatomical models tailored to specific educational needs.
Through workshops and training sessions, you’re gaining practical skills in 3D printing techniques and software that foster innovation.
Studies show five out of six research projects indicate higher satisfaction levels with 3D printed models compared to traditional methods.
You can visualize complex anatomical structures more effectively, enhancing your understanding of spatial relationships.
Most importantly, you’re participating in real-world problem solving by designing customized prosthetics and surgical tools that directly apply to future medical practice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Is 3D Printing Used in Medicine?
You’ll find 3D printing creates patient-specific implants, prosthetics, and anatomical models that improve surgical outcomes. It reduces surgery times, cuts costs, and allows rapid customization of medical instruments based on your specific needs.
Why Are 3D Printers Becoming Increasingly Popular in Industries Like Manufacturing and Healthcare?
You’re seeing 3D printers gain popularity because they enable rapid prototyping, customization, and on-demand production. They’re reducing costs, improving patient outcomes through personalized medical devices, and accelerating innovation cycles across both industries.
What Is One Way 3D Printing Is Used in the Medical Industry?
You’ll find 3D printing creates customized implants and prosthetics that perfectly fit your individual anatomy. This personalized approach greatly improves functionality and comfort compared to traditional one-size-fits-all medical devices.
When Did the Medical Field Start Using 3D Printing?
The medical field started using 3D printing in the early 2000s when you’d see synthetic scaffolds created for bladder tissue, marking the technology’s first significant breakthrough in medical applications.




Leave a Reply